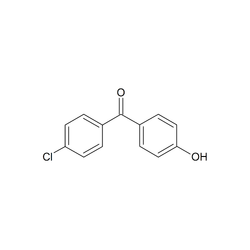
4-Hydroxybenzophenone
4-hydroxy-benzophenone
| Minimum Order Quantity | 1 Kilogram |
| Formula | C13H10O2 |
| CAS Number | 1137-42-4 |
| Melling Point | 132 - 135 Deg C |
| Molecular Weightt | 198 |
| Physical Appearance | Off White Crystalline Solid |
| Moisture Content By KF | 0.5% MAX. |
| Purity | 99% MIN |
| Packing | 25/50 Kg |
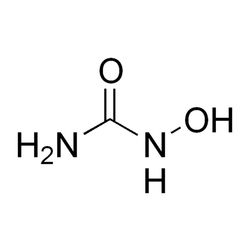
Hydroxyurea
INFORMATION OF HYDROXYUREAHydroxycarbamide (INN, BAN) or hydroxyurea (USAN, AAN) is an antineoplastic drug used in myeloproliferative disorders, specifically polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia. It is also used to reduce the rate of painful attacks in sickle-cell disease and has antiretroviral properties in diseases such as HIV/AIDS. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, a list of the most important medication needed in a basic health system.. USES Hydroxycarbamide is used for the following indications Myeloproliferative disease (primarily polycythemia vera and essential thrombocytosis). It has been found to be superior toanagrelide for the control of ET.[2]Sickle-cell disease[3] (breaks down cells that are prone to sickle, as well as increasing fetal hemoglobin content)AIDS as an adjunct to ddI in combination antiretroviral therapies[4]Second line treatment for psoriasis[5] (slows down the rapid division of skin cells)Psoriasis[6]Systemic mastocytosis[7]Chronic myelogenous leukemia (largely replaced by imatinib, but still in use for its cost-effectiveness)Biochemical research as a DNA replication inhibitor[9] that causes deoxyribonucleotide depletion and results in DNA double strand breaks near replication forks (see DNA repair).Reported side-effects are drowsiness, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea, constipation, mucositis, anorexia, stomatitis, bone marrow toxicity (dose-limiting toxicity; may take 7-21 days to recover after the drug has been discontinued), alopecia (hair loss), skin changes, abnormal liver enzymes, creatinine and blood urea nitrogen.[10] Due to its effect on the bone marrow, regular monitoring of the full blood count is vital, as well as early response to possible infections. In addition, renal function, uric acid and electrolytes, as well as liver enzymes, are commonly checked.[11] Moreover, because of this, severe anemia and neutropenia are contraindicated. Hydroxycarbamide has been used primarily for the treatment of myeloproliferative diseases, which has an inherent risk of transforming to acute myeloid leukemia. There has been a longstanding concern that hydroxycarbamide itself carries a leukemia risk, but large studies have shown that the risk is either absent or very small. Nevertheless, it has been a barrier for its wider use in patients with sickle-cell diseasE. Hydroxycarbamide decreases the production of deoxyribonucleotides[13] via inhibition of the enzyme ribonucleotide reductase by scavenging tyrosyl free radicals as they are involved in the reduction NDPs.[12] In the treatment of sickle-cell disease, hydroxycarbamide increases the concentration of fetal hemoglobin. The precise mechanism of action is not yet clear, but it appears that hydroxycarbamide increases nitric oxide levels, causing soluble guanylyl cyclase activation with a resultant rise in cyclic GMP, and the activation of gamma globin chain synthesis necessary for fetal hemoglobin production (which inhibits the formation of sickle hemoglobin aggregates). A few red cell clones called F cells are progeny of a small pool of immature committed erythroid precursors (BFU-e) that retain the ability to produce HbF.
Product Details| Minimum Order Quantity | 1 Kilogram |
| Packaging Size | As Per You required |
| CAS NO | 127-07-1 |
| Formulae | CH4N2O2 |
| Molar Mass | 76.0547 g/mol |
